(no comments available yet for this resource) |
  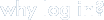
Manage your resources
Save, organize, and share resources that you find. Subscribe to bulletins Automatically be notified about new resources that match your interests. It's easy, fast, and FREE! 
AMSER =
FREE ONLINE RESOURCES for the CLASSROOM  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Copyright 2024 Internet Scout
Resource Metadata
Copyright 2024 Internet Scout
Copyright 2024 Internet Scout
http://amser.org/









Resource Comments